What is HTTP? Understanding HTTP is an application protocol for distributed, collaborative, and hypermedia information systems. HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is the basis of data communication for the World Wide Web in the form of structured text and uses logical hyperlinks between nodes that contain text. HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) has been used since 1990 and is currently undergoing version updates to improve its features. Compared to other protocols such as FTP, IMAP, SMTP and POP3, HTTP is the most used and quite popular.
Understanding HTTP According to Experts
1. Oxford Dictionaries
According to Oxford Dictionaries, HTTP is a data transfer protocol used on the World Wide Web (WWW).
2. Wikipedia
According to Wikipedia, HTTP is an application protocol for distributed, collaborative, and hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the data communication basis for the World Wide Web.
3. Techtarget.com
According to Techtarget.com, HTTP is a set of rules for transferring files (text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files) on the World Wide Web. HTTP is an application protocol that runs on top of the TCP/IP protocol suite (the basic protocol for the Internet).
HTTP Functions on the Internet
Referring to the meaning of HTTP above, HTTP has a fairly simple function, namely to connect a computer to another computer via an internet connection. HTTP is likened to a command to run every computer in order to send messages. HTTP also serves to determine how messages or data can be transmitted or formatted into other forms that can be accepted by the browser. So that all the data desired by the client can be accessed or displayed. So, HTTP will always appear on all website addresses when we open it on the internet. This is because all website services use the HTTP or HTTPS protocol to run.
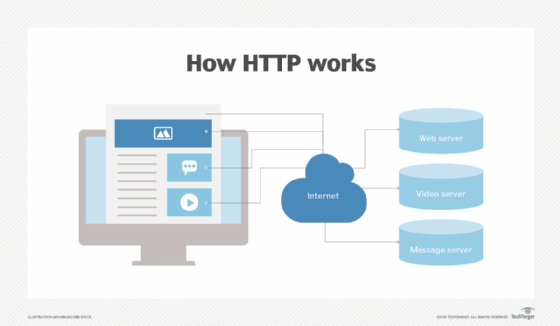
How HTTP Works on the Internet
Basically how HTTP works is quite simple. When a user opens a website through a browser, HTTP will connect the user with the WWW and also a resource known as a URL. Then HTTP will enter the protocol using TCP / IP, and then display the data obtained back into the browser. After that the user can view various sites and their contents through the browser. Briefly, how the HTTP protocol works in transmitting data can be described as follows:
- The client computer or HTTP client will establish a connection and send a document request to the web server.
- The HTTP server then processes the request and the HTTP client waits for a response.
- Finally, the web server will respond to the request via a data status code and close the connection when the request process is complete.
The need for digital IT is needed in daily activities, Bead IT Consultant is the right choice as your partner, visit our website by clicking this link: www.beadgroup.com