Definition of Mumps
Mumps is a viral infection that affects the saliva-producing glands. This gland is located near the ear. This condition can cause swelling of one or both of the glands that produce saliva. The virus that usually causes mumps is a virus from the paramyxovirus group. Mumps is a disease that can be transmitted. The process of transmission is the same as the flu, namely when a person inhales or is exposed to droplets of saliva that contain the virus. The disease, also known as mumps, affects children aged 2-12 years, who have not been vaccinated. However, it is possible for adults who have not received the vaccine to experience it.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF MUMPS
Symptoms of mild mumps
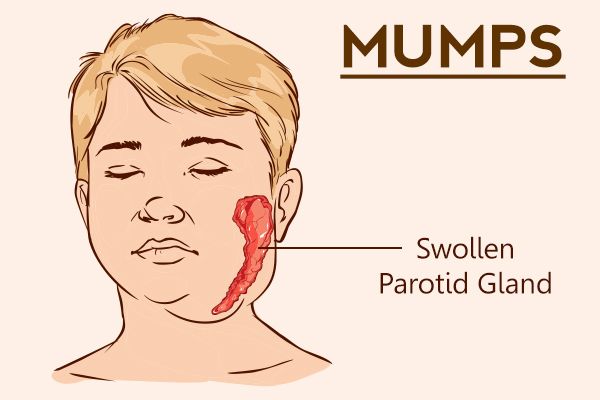
• Swelling of the salivary glands (parotid glands) causing both sides of the face to appear swollen.
• Pain in the neck muscles, the area between the ears and the lower jaw
• Headache
• High fever between 39-40°C, which can last 2-3 days
• No appetite
•Sore throat
• Pain and swelling of the salivary glands under the ear on one or both sides of the face (parotitis)
• Weakness and fatigue
• Pain when chewing or swallowing
These mild symptoms usually disappear within two weeks. In serious conditions, mumps can attack organs, such as the testes, ovaries, pancreas and brain. This condition can also cause miscarriage, deafness, and meningitis (inflammation of the lining of the brain).
Symptoms of severe mumps
• Severe headache
• Neck or neck stiffness
• Red eye
• Sleepy
• Heartburn
• Gag
• Pain or lumps in the testicles or testicles
• Seizures
If you are pregnant and exposed to someone who is experiencing mumps, consult a doctor immediately, even if you do not experience any symptoms.
Causes of mumps
The cause of mumps is a virus from the paramyxovirus group which is spread through infected saliva splashes. For example, through sneezing, coughing, and sharing eating utensils with people who have been infected.
Mumps risk factors
Some of the risk factors for this disease include:
• Children aged 2-12 years who have not received the vaccine.
• Unvaccinated adults
Mumps Diagnosis
Although it is not classified as a serious disease, it is still recommended that you or your child see a doctor if you experience symptoms of mumps. This examination to the doctor is also useful to ensure the symptoms of mumps are similar to other infections, such as tonsillitis (tonsillitis). To diagnose mumps, the doctor will usually do a physical examination, especially checking body temperature and mouth to see the condition of the tonsils and tonsils. In addition, blood tests also need to be done to detect the presence of the mumps virus.
Mumps Complications
Mumps very rarely causes complications. However, if it occurs, some complications of mumps can be serious. Most complications of mumps cause inflammation and swelling in several parts of the body, such as:
• Testes. Mumps can also cause swelling of one or both testicles, which is more common in teenage boys entering puberty. This condition is also known as orchitis. Orchitis is painful, but rarely causes infertility.
•Brain. Viral infections such as mumps can also cause inflammation of the brain (encephalitis). The condition can cause neurological problems and be life-threatening.
• Membranes and fluid around the brain and spinal cord. This condition is also known as meningitis and can occur when the mumps virus spreads through the bloodstream and infects the central nervous system.
How to treat mumps
How to treat mumps will generally depend on the severity of the disease and how long the patient has had the condition. Because it is caused by a virus, mumps usually goes away on its own and cannot be cured with antibiotics. What the patient can do is treat the symptoms to make them more comfortable. Here’s an example:
• Drink plenty of fluids to avoid dehydration due to fever
• Consume soft foods, such as porridge or soup
• Avoid eating and drinking acid because it can trigger salivary glands to feel sore
• Apply a cold compress on the swollen glands
• Take pain relievers and fever reducers, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen
• Take a break if you feel tired
Patients can also prevent transmission of the virus to others by self-isolation.
Mumps Prevention
Mumps can be prevented by giving MMR immunization to children. The vaccine is given when the child is 12-18 months old and must be repeated once again when he is 6 years old. As for adults who never got vaccinated as a child, they can take precautions by maintaining hand hygiene, not sharing toiletries or eating with other people, and wearing a mask.
For people with mumps, you should not move outside the house for a while until it heals. This is because this disease is easily transmitted to other people, especially a few days before the parotid gland swells up to a few days after. Therefore, make it a habit to cover your mouth and nose when you want to sneeze or cough, then throw the tissue away. After that, wash your hands thoroughly. By washing your hands, you can prevent the virus from sticking to other media that could potentially be touched by other people who are still healthy.
The need for digital IT is needed in daily activities, Bead IT Consultant is the right choice as your partner, visit our website by clicking this link: www.beadgroup.com